Osteopathy
What is an Osteopath?
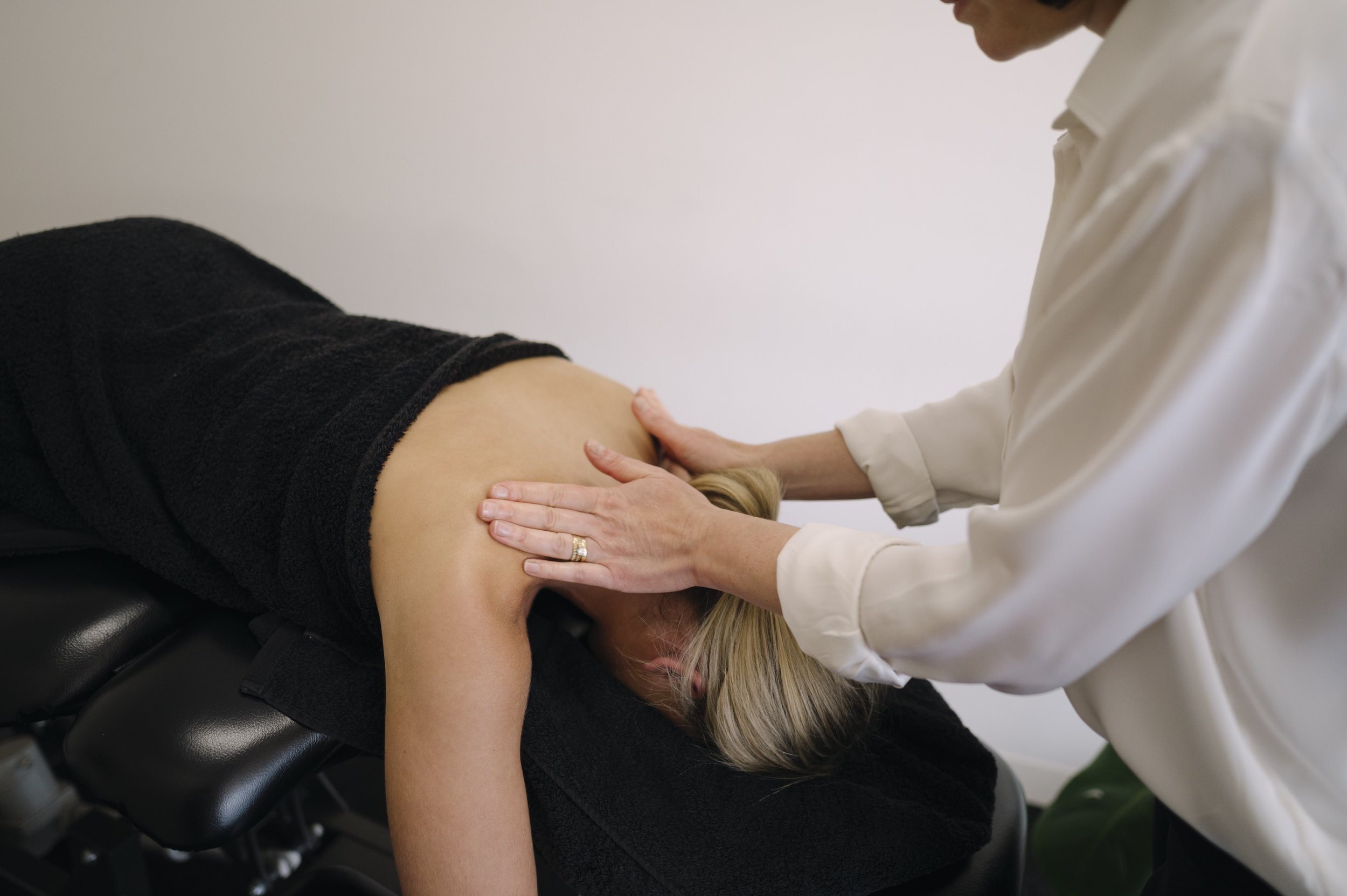
Osteopathy is a form of alternative or complementary medicine that focuses on the manual manipulation of the musculoskeletal system to promote overall health and well-being. The underlying principle of osteopathy is that the body's structure and function are interconnected, and disturbances in the musculoskeletal system can affect the body's ability to heal and maintain good health.
Osteopathic practitioners, known as osteos or osteopaths, use a hands-on approach to diagnose, treat, and prevent various medical conditions. They employ a range of techniques, including joint mobilization, stretching, and gentle pressure on muscles and tissues. The goal is to enhance the body's natural ability to heal itself and restore balance.
Osteopathy is often used to address musculoskeletal issues such as back pain, neck pain, joint pain, and sports injuries. However, some practitioners may also claim that osteopathic treatments can have broader health benefits by improving circulation, reducing stress, and supporting the body's immune system. This can help to address various concerns relating to the diaphragm (breathing), stomach, kidneys and other organs.
It's important to note that while many people report positive outcomes from osteopathic treatments, the specific health outcomes do vary from person to person. We would happily talk you through how osteopathy could benefit you and help you make a time to consult an osteopath in Lilydale.
How is an Osteo similar and different to a Physio?
Osteopaths and physiotherapists are both healthcare professionals who work to improve patients' physical well-being, but they have distinct approaches and philosophies.
Osteopath:
Philosophy: Osteopathy is based on the philosophy that the body is a holistic unit, and the musculoskeletal system, organs, and other tissues work together. Osteopaths believe that the body has self-healing mechanisms that can be facilitated through manual therapy.
Treatment Approach: Osteopaths primarily use hands-on techniques, such as joint manipulation, soft tissue massage, and stretching, to address musculoskeletal issues. They focus on improving the overall functioning of the body, considering the interconnectedness of different body systems.
Scope of Practice: Osteopaths commonly treat a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal pain, joint issues, and may also address other aspects of health, believing that dysfunction in one area can affect the entire body.
Physiotherapist:
Philosophy: Physiotherapy, or physical therapy, is rooted in the belief that physical function and movement are crucial to a person's well-being. Physiotherapists emphasize restoring and optimizing movement and function to improve a patient's quality of life.
Treatment Approach: Physiotherapists use a variety of techniques, including exercises, stretches, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation. They focus on rehabilitation, aiming to restore mobility, strength, and function. Physiotherapy often involves patient education and exercises for home management.
Scope of Practice: Physiotherapists address a broad spectrum of conditions, including musculoskeletal issues, neurological disorders, cardiovascular and respiratory problems, and more. They may work with patients of all ages and across various healthcare settings.
While there is some overlap in the conditions they treat, the key difference lies in their approach and philosophy. Osteopathy tends to have a more holistic view of the body, emphasizing the interconnectedness of different systems, while physiotherapy often focuses on specific functional goals and rehabilitation. Both professions play important roles in healthcare, and the choice between them may depend on individual preferences, the nature of the condition, or the recommendations of healthcare professionals.
Which hands-on treatments do osteopaths use in treatment?
Osteopaths use a variety of hands-on techniques to diagnose, treat, and prevent musculoskeletal issues and promote overall health. The specific techniques employed may vary depending on the individual practitioner's training, patient needs, and the nature of the condition being treated. Some common hands-on techniques used by osteopaths include:
Soft Tissue Manipulation/Massage: Osteopaths may use techniques to manipulate and massage soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and enhance tissue flexibility.
Joint Mobilization: Osteopaths employ gentle movements to mobilize and manipulate joints. This can help improve joint function, increase range of motion, and alleviate stiffness.
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET): MET involves the active participation of the patient in resisted muscle contractions and relaxation, usually against the osteopath's counterforce. This technique is used to improve joint mobility and correct muscle imbalances.
Articulatory Techniques: Osteopaths use rhythmic and repetitive joint movements to encourage improved joint function. This may involve gentle oscillations or rotations of the joint.
High-Velocity, Low-Amplitude (HVLA) Thrusts: This technique, often referred to as joint manipulation or adjustment, involves a quick, controlled movement of a joint to improve mobility and reduce joint restrictions. HVLA is one of the more distinctive features of osteopathic treatment.
Myofascial Release: Osteopaths work with the fascial system, a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, organs, and other structures. Myofascial release involves applying sustained pressure to release tension in the fascia and promote better movement.
Lymphatic Pump Techniques: These techniques aim to improve lymphatic circulation, which can be beneficial for reducing swelling and enhancing the immune system's function.
Cranial Osteopathy: This technique involves gentle manipulation of the bones of the skull and the cranial rhythm to influence the central nervous system and promote overall well-being. It's based on the idea that subtle movements in the cranial bones can affect the body's health.
It's important to note that osteopathic treatments are typically individualized based on the patient's condition, and practitioners may use a combination of these techniques during a session. Before seeking osteopathic treatment, it's advisable to consult with a qualified and licensed osteopath to discuss your specific health concerns and determine the most appropriate approach for your needs. We would happily answer your questions over the phone on 9737 6665.
How do I know if Osteo or Physio is right for me?
A: Determining whether osteopathy or physiotherapy is right for you depends on various factors, including your specific health condition, personal preferences, and the approach that aligns with your goals. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Nature of the Condition:
Osteopathy: Osteopaths often take a holistic approach, addressing the interconnectedness of different body systems. If you have musculoskeletal issues, joint pain, or are looking for a more comprehensive approach to health that considers the whole body, osteopathy may be suitable.
Physiotherapy: Physiotherapists focus on restoring movement and function, making it a good choice for rehabilitation following injuries, surgery, or specific functional impairments. Physiotherapy is applicable to a wide range of conditions beyond musculoskeletal issues, including neurological and respiratory disorders.
Treatment Approach:
Osteopathy: Osteopathic treatment involves hands-on techniques, such as joint manipulation, soft tissue massage, and myofascial release. If you prefer a manual therapy approach that considers the body as a whole, osteopathy might be a good fit.
Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy often incorporates a combination of exercises, stretches, and modalities to improve mobility, strength, and function. If you are comfortable with an active participation approach and targeted exercises, physiotherapy may be more suitable.
Personal Preferences:
Osteopathy: If you prefer a holistic and hands-on approach to healthcare and are open to the idea of addressing not just symptoms but the underlying causes, osteopathy may be appealing.
Physiotherapy: If you are more inclined towards structured exercises, rehabilitation plans, and a goal-oriented approach to improve specific functions, physiotherapy might align better with your preferences.
Healthcare Provider Recommendations:
Consult with your primary healthcare provider, such as your general practitioner or specialist, for guidance. They can provide insight into which approach may be more suitable based on your medical history and condition.
Consultation with Practitioners:
Schedule consultations with both osteopaths and physiotherapists to discuss your specific health concerns, treatment options, and their approaches. This can help you get a sense of their expertise and whether you feel comfortable with their recommended treatments.
Regulatory Considerations:
Ensure that the practitioner you choose is licensed or registered with the relevant regulatory authorities in your jurisdiction. This ensures that they have met the required standards of education and practice.
Ultimately, the choice between osteopathy and physiotherapy may involve a trial-and-error process to see which approach works best for you. Some individuals find that a combination of both therapies can be beneficial, depending on their needs. Give us a call on 9737 6665 to speak to our Lilydale clinic about how Physio and Osteo could benefit you.
Which conditions can Physios and Osteos help with?
Both Osteo and Physio help people with the following conditions:
Headache
Torticollis
Muscle disorders in the arms and legs
Pelvic problems
Jaw problems
Knee problems
Foot problems
Recurrent sprains
Pregnancy
Menstrual pain
Incontinence
Abdominal pain
Scoliosis
Rheumatic diseases
Chronic pain
Sports injuries
Consider the following articles on:
